Advanced hard disk tools: Difference between revisions
| Line 76: | Line 76: | ||
==Spinrite== | ==Spinrite== | ||
Spinrite is a sophisticated hard disk maintenance utility, which works much harder than most others in order to recover data from failing disks. In many cases, Spinrite can use the | Spinrite is a sophisticated hard disk maintenance utility, which works much harder than most others in order to recover data from failing disks. In many cases, Spinrite can use the erroneous results of many failed reads, together with error correction bits, to deduce what the data must have been. This allows Spinrite to rewrite the recovered data, causing the disk to write it to alternate spare sectors. | ||
An important distinction needs to be understood between the function of Spinrite and the DOS or Windows CHKDSK utility. The latter operates on the logical structure of the file system, i.e. how the disk space is organised as folders and files and free space is managed, simply regarding the disk as large pool of numbered blocks. It therefore cannot correct faults in the disk itself. Spinrite, on the other hand, works on the disk as a pool of blocks with no concern about how they might be used. It is therefore equally applicable to any hard disk however it's formatted, even if taken from another device such as a PVR or hard disk iPod, just so long as it can be connected to a machine that Spinrite can run on. | An important distinction needs to be understood between the function of Spinrite and the DOS or Windows CHKDSK utility. The latter operates on the logical structure of the file system, i.e. how the disk space is organised as folders and files and free space is managed, simply regarding the disk as large pool of numbered blocks. It therefore cannot correct faults in the disk itself. Spinrite, on the other hand, works on the disk as a pool of blocks with no concern about how they might be used. It is therefore equally applicable to any hard disk however it's formatted, even if taken from another device such as a PVR or hard disk iPod, just so long as it can be connected to a machine that Spinrite can run on. | ||
| Line 93: | Line 93: | ||
To understand how Spinrite achieves its magic, it's necessary to understand how hard disks handle errors. | To understand how Spinrite achieves its magic, it's necessary to understand how hard disks handle errors. | ||
The space on a hard disk is made up of sectors, each 512 or 4096 bytes long. Each has Error Correction Code (ECC) bits appended, using which the disk firmware can correct read errors up to a certain number of consecutive bits. Such errors are corrected by the disk without bothering the user or the host computer. Furthermore, if the disk finds a sector which is becoming marginal (it only just managed to correct an error) it will automatically allocate a spare sector and rewrite the data to the spare, marking the original as bad. | The space on a hard disk is made up of sectors, each 512 bytes, or for large disks, 4096 bytes long. Each has Error Correction Code (ECC) bits appended, using which the disk firmware can correct read errors up to a certain number of consecutive bits. Such errors are corrected by the disk without bothering the user or the host computer. Furthermore, if the disk finds a sector which is becoming marginal (i.e. it only just managed to correct an error) it will automatically allocate a spare sector and rewrite the data to the spare, marking the original as bad. | ||
But problems arise if an error is beyond what the ECC can correct. In this case, the disk returns an error to the host computer, and Windows will retry a few times before giving up. Should the file be overwritten, the disk will recognise that this was a troublesome sector, heave a sigh of relief that nobody wanted the data after all, and write the new data to a spare sector, marking the old as bad. | But problems arise if an error is beyond what the ECC can correct. In this case, the disk returns an error to the host computer, and Windows will retry a few times before giving up. Should the file be overwritten, the disk will recognise that this was a troublesome sector, heave a sigh of relief that nobody wanted the data after all, and write the new data to a spare sector, marking the old as bad. | ||
But if you really did want the data in the failing sector, you're out of luck unless you have a copy of Spinrite. What this does is to try very much harder than either the disk itself or Windows | But if you really did want the data in the failing sector, you're out of luck unless you have a copy of Spinrite. What this does is to try very much harder to read the data than either the disk itself or Windows, using all the tricks in the book and some more. If it eventually persuades the disk to perform a good (or at least an error-corrected) read, the disk will itself reallocate the data. However, Spinrite can often use the partial data received from many failed reads in order to reconstruct what the original data actually must have been, and writes it back, once again, causing the disk to reallocate the data to a spare sector. In the worst case, Spinrite will write back to the disk as much data as it managed to recover from the sector, as it may be that not all of the data in the sector was needed anyway. | ||
Spinrite have several operating levels, but is almost always used either in Level 2 or 4. Level 2 does its utmost to recover data and in the process will cause bad sectors to be swapped out with spares. Level 4 additionally temporarily saves the contents of each sector in a spare sector while it repeatedly rewrites the original in order to provoke a reallocation, should the sector be getting weak. | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Revision as of 19:19, 12 October 2014
Advanced tools for diagnosing and recovering hard disk problems.
Summary
The S.M.A.R.T. data returned by a hard disk can give a useful indication of its health but there are other tools that can be used which go well beyond this. WARNING: some of these tools can be DANGEROUS and should only be used in a kill-or-cure situation or if you are certain that a full system backup is available and you are sure you know what you are doing.
Speedfan
Speedfan is the easiest of hard disk tools to use. It runs under Windows and gives vital statistics of a system, such as temperatures. But a very useful additional function is that it reports SMART data, and more than that, can compare the state of your hard disk with an online crowd-sourced database to show how your hard disk is ageing compared to others of the same model. Select the S.M.A.R.T. tab and click the "Hard disk" box to select yours. Review the results, then click the "Perform an in-depth online analysis" in order to get a customised online report, which will appear in a browser window.
ddrescue
ddrescue is a linux tool for copying disks sector by sector. As such, it resembles the venerable Unix and linux utility dd but that is as far as the resemblance goes. Unlike dd, it will persist if it gets a read or write failure, and keeps a log of the blocks it has successfully processed. This makes it possible to run it multiple times, attempting to recover as much data as possible. It may therefore be a useful first tool to try in recovering data from a failing disk.
It can be installed by the shell command
sudo apt-get install gddrescue
The man ddrescue command gives full details of options.
gdisk
Gdisk is a Linux command line tool for partitioning hard disks, included as standard in some disttros such as SystemRescueCD but installable on any other. Conceptually, it is similar to the DOS fdisk command but is much more flexible, can cope with large disks, and may be able to partition or repartition a disk that other tools refuse to on account of bad sectors.
MHDD
MHDD is a low level diagnostic and maintenance tool that runs under MSDOS or FreeDOS. It's best run from a DOS bootable USB memory stick. If you have Spinrite on a memory stick, add this to it too.
Faced with a slow running computer, MHDD will show very clearly whether the problem is a failing hard disk, performing many retries in order to read data.
Note that MHDD will destroy data if not used with care.
MHDD is basically a user interface to the ATA command set and more. A key feature is that it accesses the disk direct rather than going through the BIOS and hence gets a more accurate and uncensored view. For example it can read the SMART data even if the BIOS hides it. The following is a very brief survival guide to the most useful functions.
Command line flags
\ENABLEPRIMARY
Normally MHDD disables access to the primary disk on the assumption that this may well be what DOD is running from. Use this command line flag when running from a bootable USB memory stick if it's the primary disk you need to access.
Commands
MHDD issues a prompt, to which you can type a range of commands, a few of which are listed here. (Commands are case-insensitive.)
HELP - Gives a list of commands and brief descriptions
MAN <command> - Gives a fuller description of the named command.
PORT - Issue this command first to get a list of disks, then select the one you want by number.
EID - Report extended ID information from the disk.
SMART ATT - Report values of SMART attributes. (The F8 key is a synonym for this command.) Pay special attention to:
- Read error rate
- Relocated sectors count
- Relocate event count
- Current pending sectors
See the Wikipedia S.M.A.R.T. article for further details, and also below.
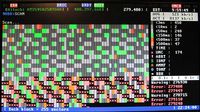
SCAN - Scan the disk
The disk is scanned, giving a graphic display of its state, and with the option of remapping bad sectors.
Several options are offered in a pop-up menu, in particular:
- Start, End - Start and end sectors for the scan, defaulting to the entire disk.
- Remap - Attempt to remap bad sectors, provided they can be read correctly (with difficulty).
- Erase delays - Erase sectors which take a long time to read, whether or not correctly. This should cause them to be remapped, but the data is lost.
To make sense of the Remap and Erase delays options, the criteria for a drive to automatically remap (or relocate) are normally roughly as follows, though they may vary:
- If a read is eventually successful after retries and/or error correction, then if the retries and/or error correction were below a certain threshold, do nothing.
- If the retries and/or error correction were above that threshold, but the data was eventually recovered, remap the sector (rewrite the data to a spare sector and mark the original unreadable).
- If the data couldn't be recovered, mark the sector as "unstable", increment the count of "pending" sectors and return an error to the host computer.
- If the sector had already been marked unstable but is now read correctly, remap it and decrement the "pending sectors" count.
- If a write occurs to a sector marked as "unstable", remap it by diverting the write to a spare sector and decrement the "pending sectors" count.
Blocks of 255 sectors are each represented n the graphic display by a single blob. A brighter greyscale or a coloured blob indicates a slow read, suggesting the disk had trouble reading a sector. An "x" indicates a sector was unreadable.
Log files
Log files of a session are created in a sub-folder LOG in text format. Rename the LOG directory after a session so that a new session on a different disk and on another occasion will create new log files.
Spinrite
Spinrite is a sophisticated hard disk maintenance utility, which works much harder than most others in order to recover data from failing disks. In many cases, Spinrite can use the erroneous results of many failed reads, together with error correction bits, to deduce what the data must have been. This allows Spinrite to rewrite the recovered data, causing the disk to write it to alternate spare sectors.
An important distinction needs to be understood between the function of Spinrite and the DOS or Windows CHKDSK utility. The latter operates on the logical structure of the file system, i.e. how the disk space is organised as folders and files and free space is managed, simply regarding the disk as large pool of numbered blocks. It therefore cannot correct faults in the disk itself. Spinrite, on the other hand, works on the disk as a pool of blocks with no concern about how they might be used. It is therefore equally applicable to any hard disk however it's formatted, even if taken from another device such as a PVR or hard disk iPod, just so long as it can be connected to a machine that Spinrite can run on.
Spinrite is designed for use with conventional (spinning) hard disks and should not normally be used on solid state disks (SSDs) as it will cause unnecessary wear to the memory cells. However, it can be used on Level 2, (read-only data recovery) which doesn't cause wear and can force an SSD to reallocate marginal cells. There have been multiple reports of this resulting in an SSD regaining its as-new performance after having become slow.
Spinrite runs under MSDOS or FreeDOS and comes as a bootable CD image or .exe file, but is quite easily installed on a bootable memory stick. It costs $89 for a personal licence but comes with a no quibble satisfaction or money back guarantee. You may find a Restarter at a Restart Party who has a copy.
A drawback of Spinrite is that it can take many hours to run to completion, especially if it has to work hard to recover data. However, a computer which fails to boot may be suffering from a bad sector in the first few hundred MB, which it may be able to repair in much less time.
A new version of Spinrite is expected during the second half of 2014 which will use very much larger buffers in order to achieve a very considerable increase in operating speed. It should also include enhancements to free it from the DOS dependence, allowing it to be run on a MAC. A suspend mode, too, is expected, which should allow it to be started during a Restart Party and then put into a low power state to give the owner time to take it home and plug it in to complete.
Spinrite has been around for many years, and the current version 6.0 was released 10 years ago. An Internet search may reveal criticisms of of it, some of it vituperous. Nevertheless, whether or not it will fix the disk you are faced with today, many unsolicited testimonials indicate that it remains a useful tool.
Under the Hood
To understand how Spinrite achieves its magic, it's necessary to understand how hard disks handle errors.
The space on a hard disk is made up of sectors, each 512 bytes, or for large disks, 4096 bytes long. Each has Error Correction Code (ECC) bits appended, using which the disk firmware can correct read errors up to a certain number of consecutive bits. Such errors are corrected by the disk without bothering the user or the host computer. Furthermore, if the disk finds a sector which is becoming marginal (i.e. it only just managed to correct an error) it will automatically allocate a spare sector and rewrite the data to the spare, marking the original as bad.
But problems arise if an error is beyond what the ECC can correct. In this case, the disk returns an error to the host computer, and Windows will retry a few times before giving up. Should the file be overwritten, the disk will recognise that this was a troublesome sector, heave a sigh of relief that nobody wanted the data after all, and write the new data to a spare sector, marking the old as bad.
But if you really did want the data in the failing sector, you're out of luck unless you have a copy of Spinrite. What this does is to try very much harder to read the data than either the disk itself or Windows, using all the tricks in the book and some more. If it eventually persuades the disk to perform a good (or at least an error-corrected) read, the disk will itself reallocate the data. However, Spinrite can often use the partial data received from many failed reads in order to reconstruct what the original data actually must have been, and writes it back, once again, causing the disk to reallocate the data to a spare sector. In the worst case, Spinrite will write back to the disk as much data as it managed to recover from the sector, as it may be that not all of the data in the sector was needed anyway.
Spinrite have several operating levels, but is almost always used either in Level 2 or 4. Level 2 does its utmost to recover data and in the process will cause bad sectors to be swapped out with spares. Level 4 additionally temporarily saves the contents of each sector in a spare sector while it repeatedly rewrites the original in order to provoke a reallocation, should the sector be getting weak.
References
External links
- External links as bullet points